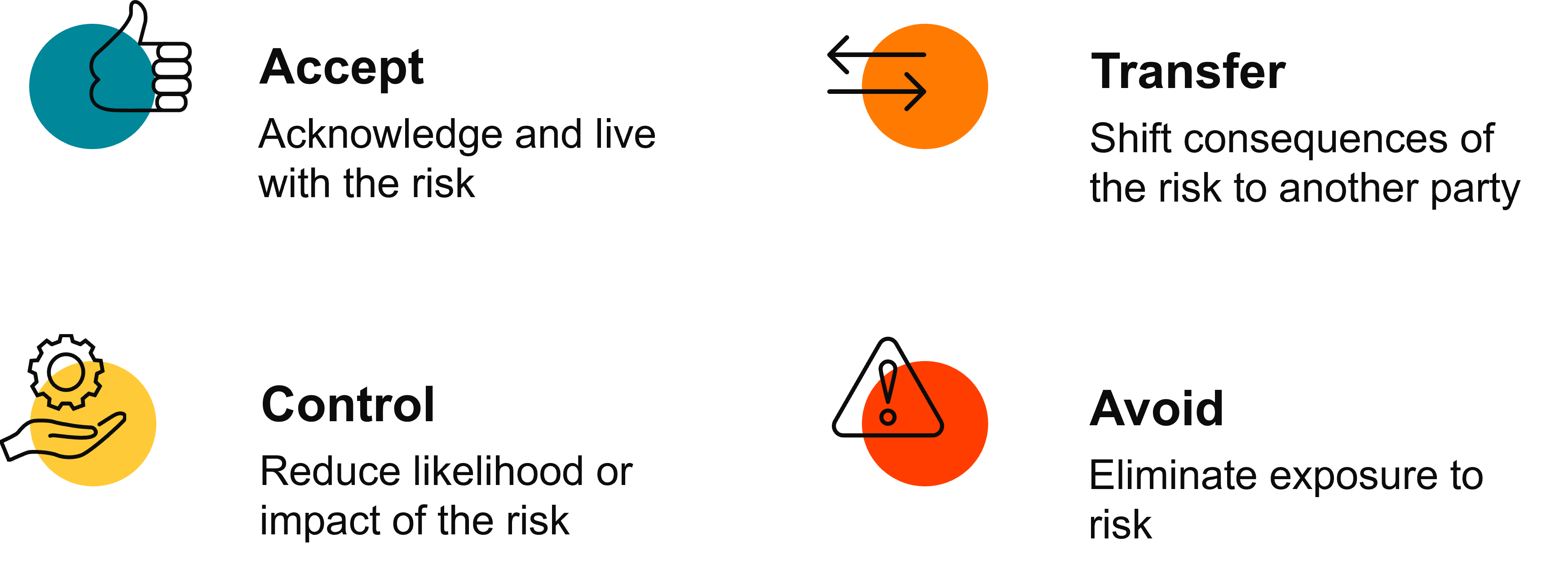
Accepting Risk
Accepting cyber risk involves acknowledging the potential consequences of a cyberattack and choosing not to invest in mitigating that risk, typically in scenarios where the potential damage is minimal or the cost of prevention exceeds the risk. This approach can be appropriate for low-priority assets or when the business impact of a breach would be insignificant.
For example, a small e-commerce company might accept the risk of downtime on a low-traffic informational website that doesn’t store customer data. Since the website is not critical to operations and doesn’t contain sensitive information, the company might decide not to invest in expensive security measures for this particular asset. Instead, it focuses its resources on protecting its e-commerce platform, where customer payment data is processed.
Transferring Risk
Transferring cyber risk involves shifting the responsibility of managing the risk to a third party. This can be done by purchasing cybersecurity insurance or outsourcing security functions to a managed service provider. It’s a viable option when the potential damage is significant, but the cost of managing the risk internally is too high. For example, a business might invest in cyber insurance to cover financial losses from a data breach, or hire an external security firm to handle advanced threat detection and response. This approach allows organizations to mitigate risk without bearing the full burden of managing it in-house.
Controlling Risk
Controlling cyber risk means taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of a cyberattack. This strategy is suitable when the potential damage is significant and the cost of mitigation is justifiable. For example, purchasing Managed Detection & Response (MDR), enabling two-factor authentication, and encrypting sensitive data are common controls that lower the risk of unauthorized access to critical accounts or systems.
By implementing these preventive measures, businesses can minimize the chance and impact of a successful breach.
Avoiding Risk
Avoiding cyber risk means steering clear of activities that carry a high potential for cyberattacks. This approach is most appropriate when the potential damage is significant and the cost of prevention is too high. A stronger example would be a healthcare provider choosing not to store patient records on internet-facing systems to avoid the risk of a data breach. Instead, they might use a closed, internal network to ensure sensitive medical data remains secure, even though this limits accessibility. By avoiding certain risky activities, businesses can significantly reduce the chances of a major cyber incident.
Cyber Risk Management In Action
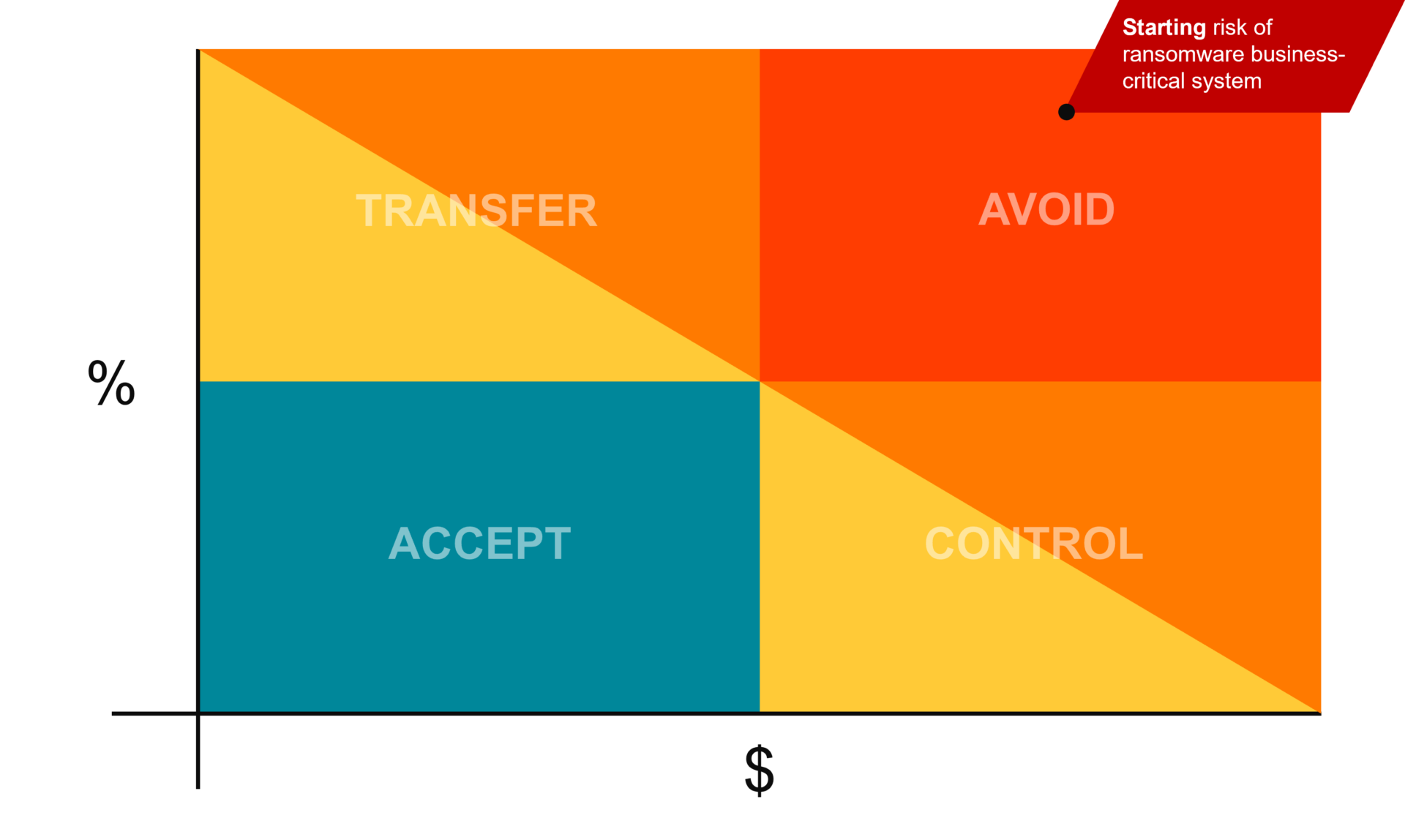
Let’s work through an example of a major risk – ransomware of a business-critical system. The inherent risk of a ransomware attack is very high, if you do nothing it is likely and it will have a major impact placing it squarely in the avoid quadrant. Now we need to manage this risk.
Starting Risk
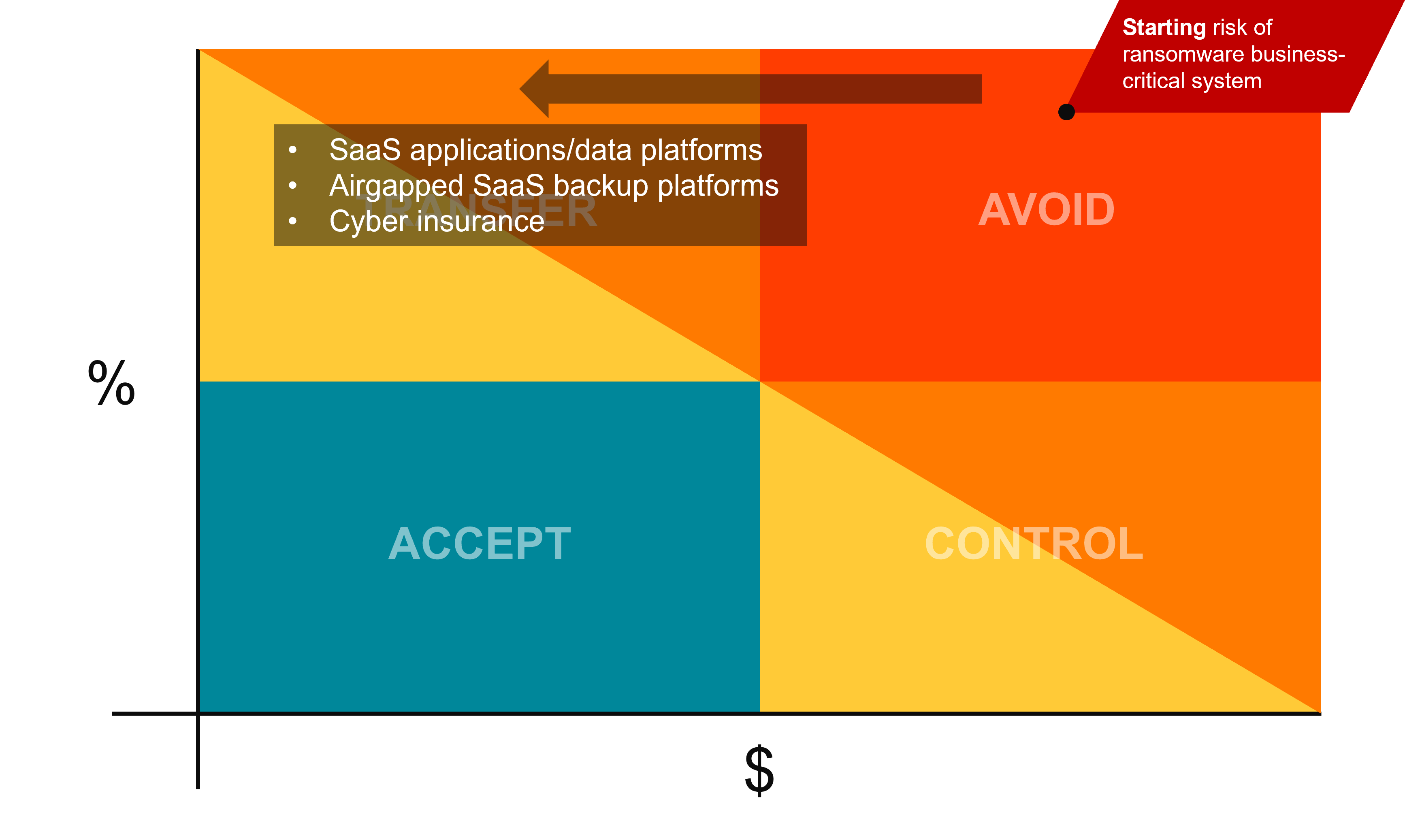
Transfer the Risk
The first risk management tool we can employee is risk transfer. You can purchase cyber insurance to control the impact of the attack, you take a huge unknowable cost and lower it to a predictable monthly insurance premium. You can subscribe to SaaS tools or outsource IT management to a 3rd party so that it becomes their responsibility to control that risk.
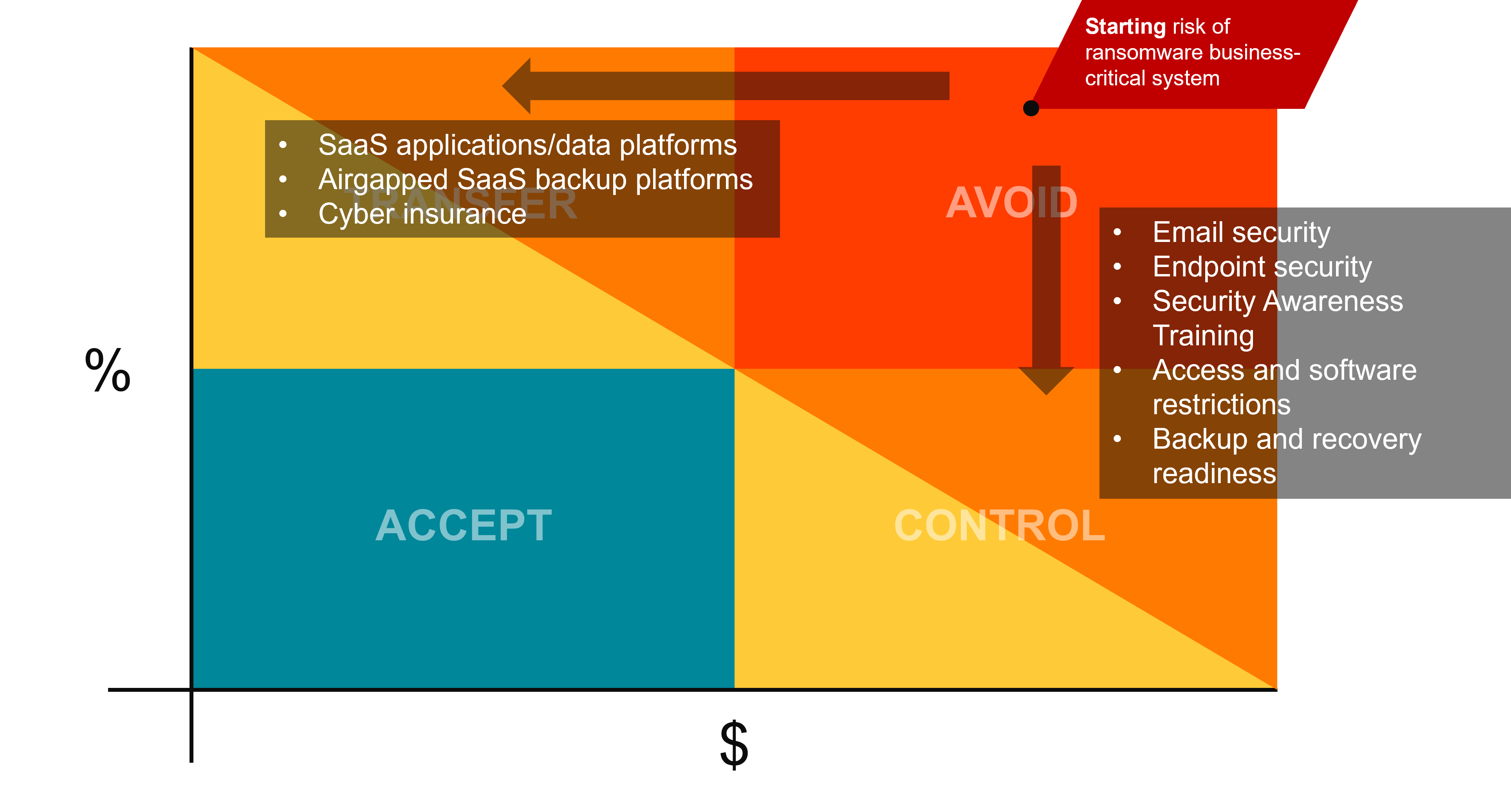
Control the Risk
Now you can reduce the chance of that risk occurring by implementing security controls. You can use these risk tools in-tandem; you can limit the impact of a ransomware attack by purchasing cyber insurance (x-axis), now you need to reduce the chance of it happening (moving down the y-axis). Employ modern security tools and best practices such as security awareness training, email and web filtering, and MFA to reduce the chance of a successful attack on your organization.
> Related 11 Security Elements That Are Non-Negotiable | Aldridge
Accept the Risk
Now you have reduced the impact and likelihood of a ransomware attack on a business-critical system. You can never fully eliminate some risks, but because you’ve employed risk management tools – you’ve brought down the managed risk of a ransomware attack to something that you can live with. If you’re breached it won’t be fun, but it won’t be devastating.
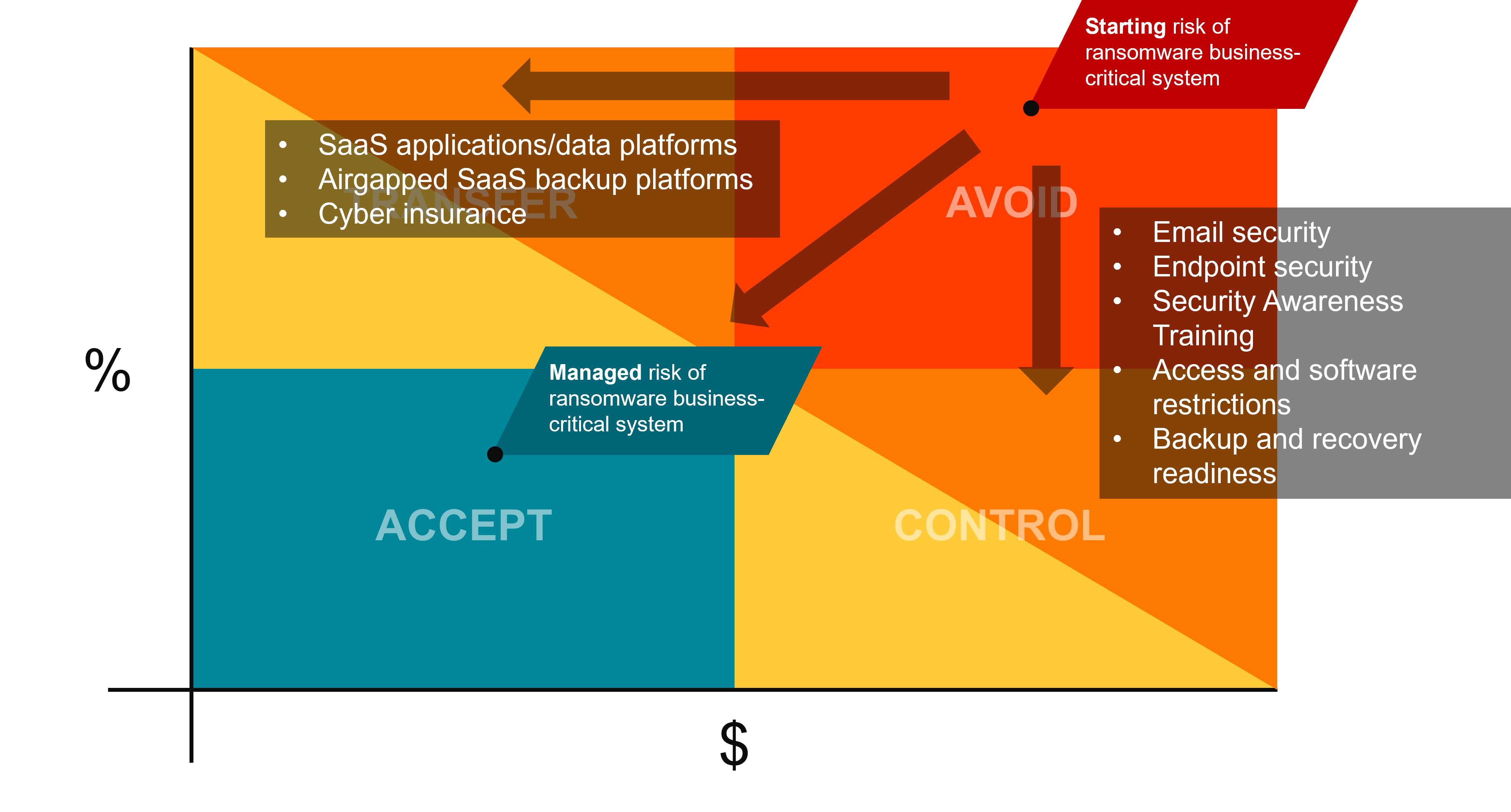
In conclusion, managing cybersecurity risk is critical to protecting your personal and business assets. By using the four tools available for managing cybersecurity risk, you can determine which approach to take based on the likelihood and potential impact of a cyber-attack, as well as the cost of prevention, control, transfer, or avoidance. Starting with a high risk is common, but implementing reasonable controls can reduce the risk and help protect against cyber threats.
State of Cybersecurity: You Will Be Breached
Learn about today’s threats, how to effectively manage your cyber risk, and 4 steps you can take today to prepare your business from what’s coming next: 2023 State of Cybersecurity | You Will Be Breached






