Employee IT security awareness training is no longer a nice-to-have; it’s mandatory.
Modern IT security requires business leaders to do more than select the right security tools for their business.
When protecting your company’s data, your employees are your most significant threat and most excellent defense. Employees falling for social engineering attacks (e.g., phishing and baiting) contributed to 33% of all data breaches (Verizon DBIR 2019). Business leaders who aren’t combining IT security policies, procedures, employee education, and testing are putting their clients and entire businesses at risk.
In today’s world, it’s not a matter of if a cyberattack will target your business, but when. The sections below explain the security threats facing your business and how security awareness training, paired with the right technology and processes, can help your business prepare for the inevitable.
Who is at Risk of a Cyberattack?
Any company could target a social attack; however, hackers tend to target small businesses. Small businesses are an appealing target for hackers and scammers because they often aren’t adequately equipped to fend off their attacks.

Creating a secure IT environment for your company can be challenging for small businesses because it requires extensive technical knowledge and can be costly. As a result, many small businesses are moving towards outsourcing their IT security needs. By outsourcing or using managed services, you have access to the required technical expertise without the cost of setting up and maintaining a secure IT environment yourself.
What’s the Business Impact of a Cyberattack?
To keep it brief, data breaches are costly. A successful phishing attack against a small business will cost them, on average, $54,000 (Small Business Trends). For mid-size companies, the financial impact increases to $1.6 million per successful attack (Enterprise Phishing Resiliency and Defense Report). If you plan on growing your company, IT security needs to be a priority. As your company increases in size, the financial damage will scale exponentially.
Poor IT security practices can devastate the value of your brand.
If you have multiple data breaches, your company may gain a reputation for being untrustworthy when handling customer information. Consumers are becoming more aware of the importance of protecting their data and employees. You may lose current and potential customers or staff members if they associate your brand with a data compromise.
What is Social Engineering?
Social engineering targets the human element of an organization. Social attacks aim to manipulate an individual to divulge confidential or personal information. That information can then be used for nefarious purposes (i.e., hacking, blackmail, etc.). Phishing and baiting are examples of effective social engineering attacks.
What is Phishing?
Phishing attacks are designed to trick a target into divulging their privileged information. Phishing attacks can be carried out through email, text, and even phone calls. A phishing attack can appear to be a routine email from HR, a client, your boss, etc. However, scammers spend considerable time making their attack look legitimate and safe to their target. That is why it is critical to train your employees to scrutinize anything that asks for their information.
Spear Phishing
There is a growing trend of scammers targeting well-researched victims by posing as someone they would trust; spear phishing. Phishing involves casting a wide net of relatively low effort attacks, while spear phishing aims at targeting fewer people with a more sophisticated attack. Spear phishing is becoming so prevalent that it makes up 71.4% of all targeted attacks (Symantec Internet Security Threat Report 2018).
An example of spear phishing could be an email sent to an employee from their company’s CEO requesting an immediate electronic transfer of funds. The scammer will leverage the employee’s obligation to follow orders from an executive and a sense of urgency to scare the target into wiring the money without confirming the request with the CEO via phone or in person. Spear phishing is becoming a serious threat to every business, substantial businesses. The cost of a successful spear-phishing attack against a large organization is $7.2 million (VadeSecure). Today’s businesses can’t afford to have poor IT security.
How to spot a phishing email
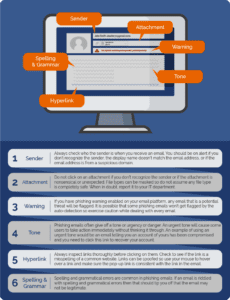
What is Baiting?
Although less common than phishing, Baiting is still a threat to any business. Baiting takes advantage of a person’s curiosity or greed to persuade the target to give up personal information or inadvertently install malware on their computer. Baiting can be done online or through physical media. An example of an online baiting scam would be a link that promises free music or movies when clicked. However, if someone clicked the link, they would install malware onto their computer.
Physical Baiting
Baiting is not just done through the internet. There have been cases of baiting being done using physical media or devices. For example, hackers have strategically left malware-infected USBs in high-traffic public areas like coffee shops, hoping someone will plug the infected machine into their computer. As soon as the USB is connected to their computer, any information on that device is vulnerable. Even though a physical baiting scam is far less likely than other forms of social engineering, it is essential to educate your staff on the dangers of connecting unknown devices to their computers.
How to Protect Your Business from Social Engineering
Today, anti-virus software alone will not protect your company from hackers. Instead, a secure IT environment relies on a combination of:

If any of the above components are lacking, your business is at a greater risk of being successfully hacked.
Employee Security Awareness Training
Many companies focus heavily on protecting their data from external threats; however, the time and money invested in data security are wasted if your employees hand over your company’s data to hackers themselves.
Your employees have access to information vital to your company’s survival, so it is critical that your IT department consistently educates and trains your staff on IT security best practices. Familiarizing your employees with common scams, such as phishing and baiting, and teaching them what warning signs to look out for (i.e., entering personal information, clicking unknown links, etc.) will go a lot further than implementing the most expensive and cutting edge IT security tools. Yes, updated technology and tools are necessary, but they are not the whole package.
Security Policies & Procedures
Supporting your employee’s IT security efforts on an institutional level is key to a secure IT environment. Your IT department needs to create an easy-to-follow procedure for how your employees deal with a potential phishing or baiting attack.
An example of a phishing email procedure could be:
- An employee receives a suspicious email
- Employee reports email to the IT department
- IT department sends a company-wide warning about the potential phishing email
- IT department conducts an audit to determine if there was a data breach
Security Breach Response Planning
You must plan for the worst and have a procedure for dealing with a potential data breach. Your company will not have time to sit around and strategize for each incident. Fifty percent of phishing-attack victims open the email and click the phishing link within 1 hour of the email being sent (Verizon DBIR). Hackers will be ready to extract any of your company’s data as soon as they have access; time is not on your side. Having set procedures that your employees are trained on will allow you to quickly react to any IT security emergency. It could save your company from a financial and PR nightmare.
IT Security Software
IT security software is most effective when your employees are educated on cybersecurity, and there are company policies and procedures to support them. Relying solely on your security software is not enough against modern hacking methods; you need to utilize your employees.
An example of security software effective against social engineering attacks is Microsoft’s Advanced Threat Protection (ATP). Some of ATP’s offerings include email links and attachment protection. ATP’s link protection will warn your employees if they click on a malicious link, and attachment protection will scan attachments from unknown users to ensure it is safe.
Routine Security Awareness Testing
Your employees’ IT security training and policies are only helpful if they can readily access and act upon that information. The only way to ensure your employees know what you need them to know is to test them. If your IT department isn’t routinely testing your employee’s knowledge of security threats and understanding of company procedures, your company is vulnerable to an attack.
There are many great tools your IT department can use to test your employee’s cybersecurity knowledge. For example, at Aldridge, we use a tool called KnowBe4. KnowBe4 allows you to send test phishing emails to your employees.
The primary benefit of testing your employees is seeing which employees are susceptible to social engineering attacks. Employees who fall for social engineering attacks can be offered additional training resources and support. In addition, if you know what your company’s weak points are, you can take steps to fortify them before it’s too late.
An additional benefit of regular training is that it creates top-of-mind awareness of IT security for your employees. When topics such as social attacks and data breaches are regularly discussed, your employees will take extra caution when they find themselves in a potentially dangerous situation.
Next Steps
Building your cybersecurity defense can be overwhelming. Don’t go at it alone. Our IT support team can help you create a best-fit plan to defend against and respond to today’s cyberthreats facing your business.







