In the early days of cyber insurance, carriers were much more relaxed about writing policies. They didn’t have a good understanding of the risks involved, and as a result, they lost a lot of money on their cyber policies.
Carriers have finally caught on to the real risk and cost of cybercrime and have begun raising their security requirements of their insured. To get a cyber policy today you will have to fill out a questionnaire, providing a detailed explanation of all your security tools and processes. Through these questionnaires, a set of core security controls has been established. If you are missing any of these 5 controls, your application may get rejected.
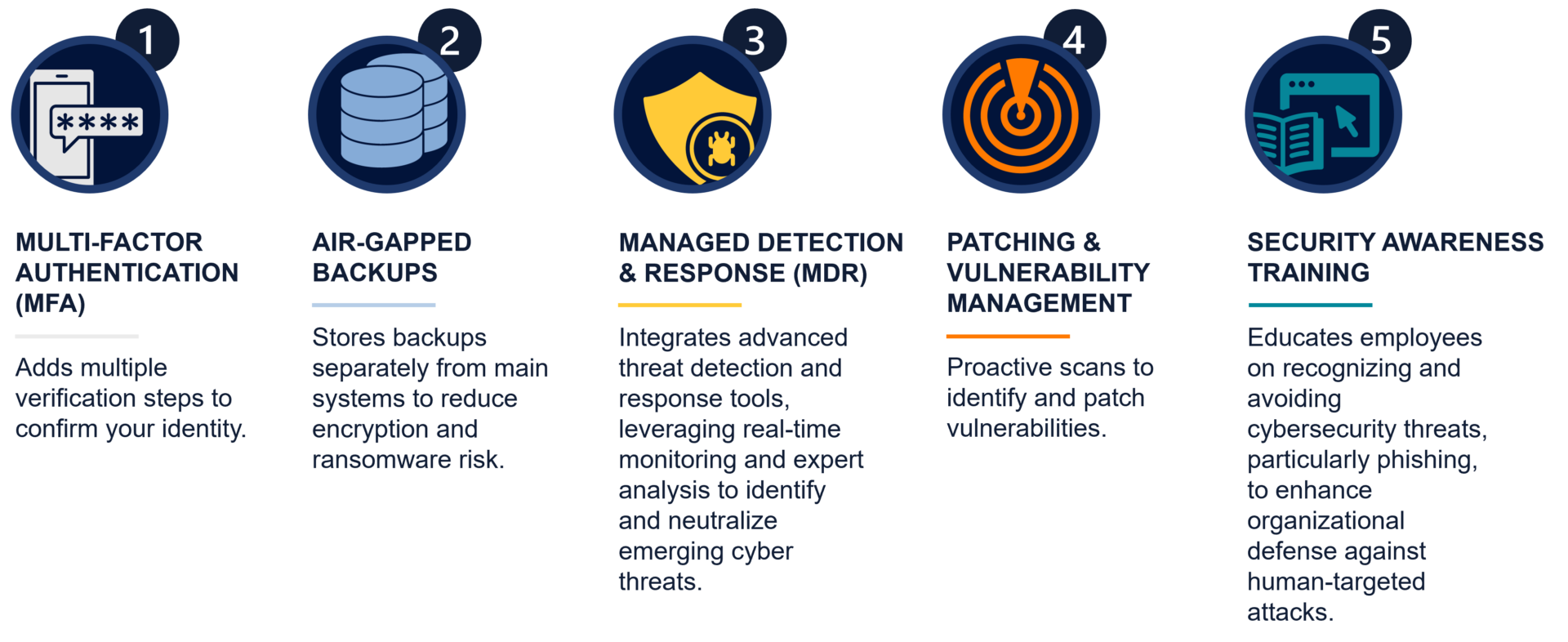
Cyber Insurance Requirements: 5 Core Security Controls
1. Multi-Factor Authentication
In the wake of high-profile data breaches, many companies have begun to require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for cybersecurity. MFA helps protect sensitive data by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple factors.
The most common form of MFA requires users to provide passwords, fingerprints, or other biometric identifiers. However, other forms of MFA can also be used, such as requiring a user to possess both a physical token and a knowledge-based factor (such as a PIN).
If you already have MFA, consider upgrading to Conditional Multi-Factor Authentication. Conditional MFA adds an extra layer of security by activating MFA prompts based on risk factors like logging in from a new location, new device, or logging in from countries you don’t typically work in. For instance, Conditional MFA might require additional verification only when users log in from an unfamiliar location or device, enhancing security without disrupting low-risk access. As cyber insurance standards become stricter, implementing Conditional MFA helps companies meet these security requirements, while maintaining a convenient work experience for their team.
2. Air-gapped Backups
Many believe a single data backup is enough to protect them from potential cyberattacks. However, this is not the case. To be fully protected, it is important to keep your backups separate from your environment. If one backup is compromised, you will still have another safe copy. Furthermore, it is also important to have backups in different locations. This way, your data will still be safe if one location is attacked. Having separate backups is essential to getting cyber insurance. Without it, you are at a much higher risk of being left without protection if your data is compromised.
3. Endpoint Detection & Response/Managed Detection & Response (EDR/MDR)
One key factor to consider is whether your organization has adequate endpoint detection and response (EDR) or managed detection and response (MDR). EDR and MDR are critical components of any effective cybersecurity program, as they can recognize and shut-down high-risk or unusual behaviors. To understand how MDR works, read how our MDR protected us from a zero-day cyber attack.
EDR refers to the tool itself, while MDR is a service where security analysts will monitor your EDR tool and investigate/respond to threats.
4. Vulnerability Management
A vulnerability is a flaw or weakness in an information system, system component, or application a threat actor can exploit to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or systems. Vulnerability scanning is the practice of detecting vulnerabilities, and vulnerability management is the process of classifying uncovered risks and remediating them to close the vulnerability. Vulnerability scanning and management is a continuous process your organization should embed in your overall security posture, and be conducted on a quarterly basis at a minimum.
Vulnerability scanning is a critical component of vulnerability management.
It helps organizations identify vulnerabilities in their network before attackers can exploit them. You should conduct external vulnerability scanning periodically to identify any weaknesses external threat actors could exploit. You should conduct internal vulnerability scanning more frequently to identify weaknesses internal users with malicious intent could exploit.
Cyber insurance policies typically require companies to have an active and comprehensive vulnerability management program to qualify for coverage. Cyber insurance providers view vulnerability management as essential to risk mitigation and prevention.
5. Security Awareness Training & Testing
To qualify for cyber insurance, businesses must implement a security awareness training and testing program. This ensures employees are up to date on security threats and procedures, and as a result businesses can reduce their risk of falling for phishing attacks. Conducting regular mock phishing campaigns does two things; it reinforces their security awareness training, and it instills a baseline level of vigilance towards their emails. Whenever your team sees suspicious emails, they are going to avoid clicking on anything because no one wants to fail a test phishing email and get enrolled in additional training.
As a leader, phishing testing is an excellent way for you to understand your team’s susceptibility for phishing attacks. Your first test will establish your baseline fail rate, and the security awareness of specific people or teams. As you train your team and build a security-minded culture, your phishing test fail rates should reflect that effort and decrease.
Quick Summary: 5 Cyber Insurance Security Requirements
Cyber Insurance Requirements – The Bottom Line
Cyber insurance is a complex topic, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. However, having core security controls is essential for businesses of any size. Whether your company is large or small, ensuring you have these core security controls is critical to protecting against cyber threats and meeting insurance requirements.
For larger organizations or those with higher risk (i.e., regulated industries), cyber insurance carriers are asking for advanced controls beyond the 5 core controls. Carriers are requiring Privileged Access Management (PAM) for business-critical systems, advanced threat detection tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), and a 24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC) to monitor your threat detection toolset.
It is important to recognize that cyber insurance requirements are evolving every year. Many security measures currently required for larger organizations may soon become standard for all businesses, regardless of size. Today carriers require these 5 core security elements, but by your next renewal this list may grow to 10 elements. It is important that you stay up-to-date on security best practices so that you’re not scrambling to catch up next time you are applying for cyber insurance.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive up to date security information and stay ahead of your cyber insurance carrier’s requirements.






