Cybersecurity breaches are an increasingly common problem for businesses of all sizes. Organizations rely heavily on technology and digital systems to store sensitive information and run critical operations. As a result, the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches is always present, and it is crucial for businesses to understand the different levels of severity that these incidents can have.
Cybersecurity breaches: Understanding the different severity levels
What Does it Mean to be “Breached”? | Aldridge
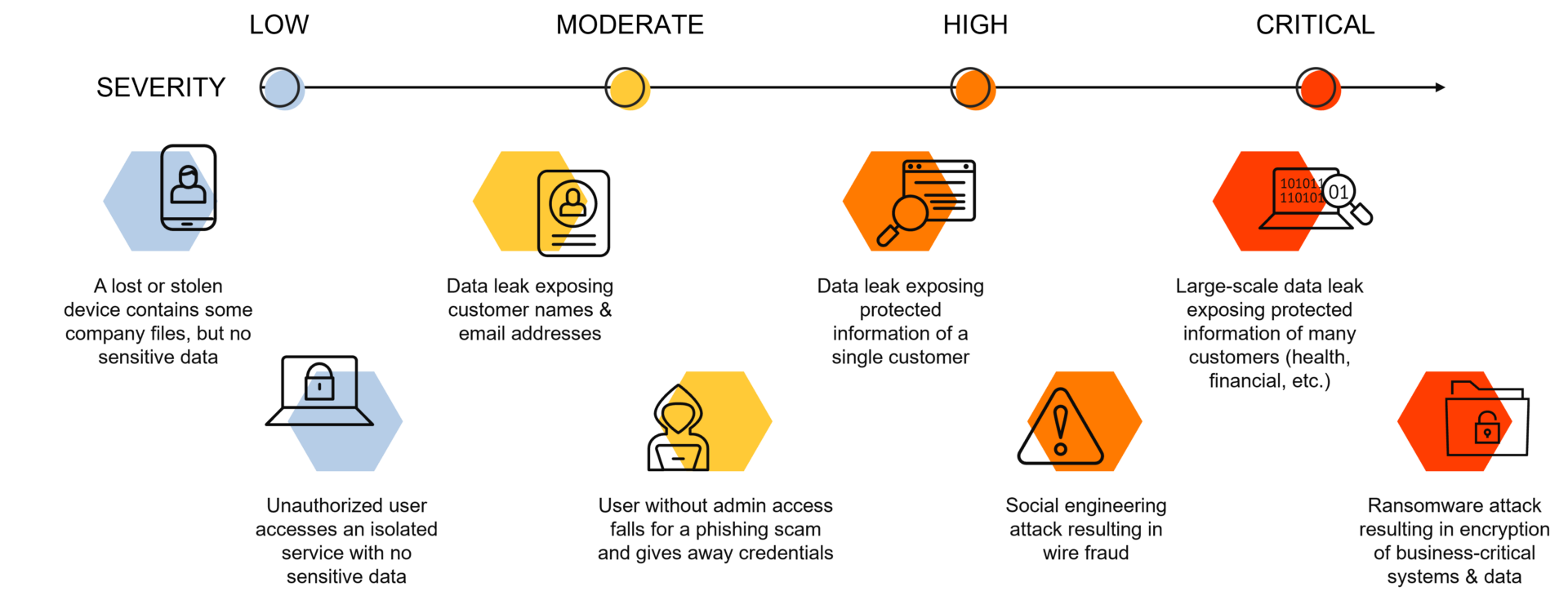
Low severity incidents
Low severity incidents are typically minor events that cause minimal disruption to business operations. These incidents may include spam emails, phishing attempts, or minor network outages. While these incidents may be frustrating, they do not pose a significant risk to sensitive data or critical systems.
Example:
An unauthorized individual gains access to the website’s customer database through a vulnerability in the outdated e-commerce platform. The attacker manages to obtain a list of customer email addresses and names. However, the breach does not expose any sensitive financial data like credit card information or passwords because the website doesn’t store that kind of information. In this case, the company experiences a low severity cyber breach.
Moderate severity incidents
Moderate severity incidents are events that disrupt normal business operations, but do not result in significant damage or loss. Examples of moderate severity incidents include a virus outbreak, a malicious insider attack, or a data leak. These incidents can cause widespread disruption and may require a significant amount of time and resources to resolve, but they generally do not pose a major threat to sensitive data or critical infrastructure.
Example:
An attacker successfully compromises a third-party vendor’s system that provides customer support chat functionality integrated into the bank’s website. The attacker gains unauthorized access to the chat logs, which include sensitive customer information such as names, contact details, account numbers, and transaction histories. The breach affects a significant number of customers, but it does not involve access to financial credentials like passwords or credit card details. In this case, the bank experiences a moderate severity cyber breach.
High severity incidents
High severity incidents pose a significant risk to sensitive data and critical infrastructure. These incidents may result in data breaches, ransomware attacks, and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). High severity incidents can cause widespread damage and may result in the loss of sensitive information, including financial data, personal information, and intellectual property.
Example:
An attacker manages to exploit a vulnerability in the company’s customer portal, allowing them unauthorized access to the customer’s account. The breach provides the attacker with access to sensitive information, including the customer’s name, home address, social security number, date of birth, and credit card details. The attacker may also gain access to the customer’s call logs, browsing history, and other communication records.
Critical severity incidents
Critical severity incidents are the most severe form of cybersecurity breaches and result in widespread damage and severe consequences. These incidents can include widespread data theft, major infrastructure failure, and complete loss of access to critical systems. These incidents can result in severe financial losses, reputational damage, and can even compromise the safety and security of the public.
Example:
Sophisticated hackers manage to infiltrate the company’s network by exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in the outdated server software. Once inside, they gain access to the entire patient database, compromising the confidentiality and privacy of the sensitive medical information. The breach exposes not only personally identifiable information such as names, addresses, and social security numbers but also detailed medical histories and potentially sensitive diagnoses.
Businesses need to be aware of the different levels of severity that cybersecurity breaches can have and take the necessary steps to protect their systems and data from attacks. This may include implementing security measures using the 4 steps to protect your business. By being proactive and taking the threat of cyber-attacks seriously, businesses can minimize the risk of damage and minimize the impact of a potential breach.
Protect your Business
Security isn’t just about prevention anymore – it is now a given that you will eventually get breached. Watch the 2023 State of Cybersecurity webinar to learn about today’s threats, how to effectively manage your cyber risk, and 4 steps you can take today to prepare your business from what’s coming next.







